In a category of uncommon disorders known as gestational trophoblastic neoplasm (GTN),
after conception, abnormal trophoblast cells proliferate inside the uterus. A molar pregnancy,
an abnormal type of pregnancy in which the fertilized egg develops into a mass of cysts
rather than a typical fetus, generally leads to the development of GTNs. Age, several genetic
variables, and a history of molar pregnancy are risk factors for GTN. Hydatidiform mole,
invasive mole, choriocarcinoma, and placental site trophoblastic tumor are some of the
several forms of GTNs.
Gestational trophoblastic disease or other disorders may be to blame for these and other signs
and symptoms and these are:
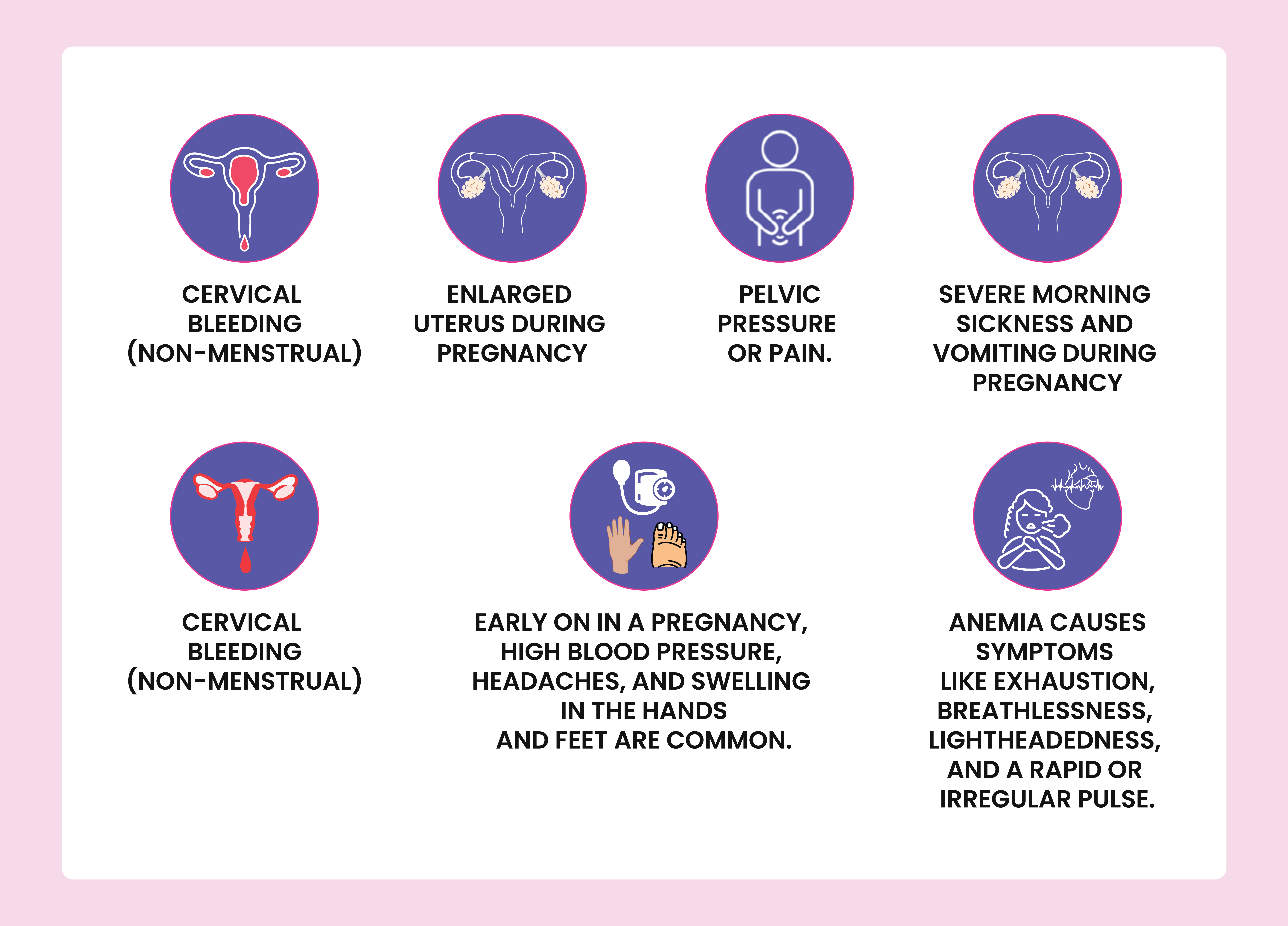
- Bleeding from the cervix unrelated to menstruation.
- A uterus that grows bigger than usual while pregnant.
- Pelvic pressure or pain.
- Severe morning sickness and vomiting while pregnant.
- Early on in a pregnancy, high blood pressure, headaches, and swelling in the hands and feet are common.
- Bleeding in the uterus after delivery that lasts longer than usual.
- Anemia causes symptoms like exhaustion, breathlessness, lightheadedness, and a rapid or irregular pulse.