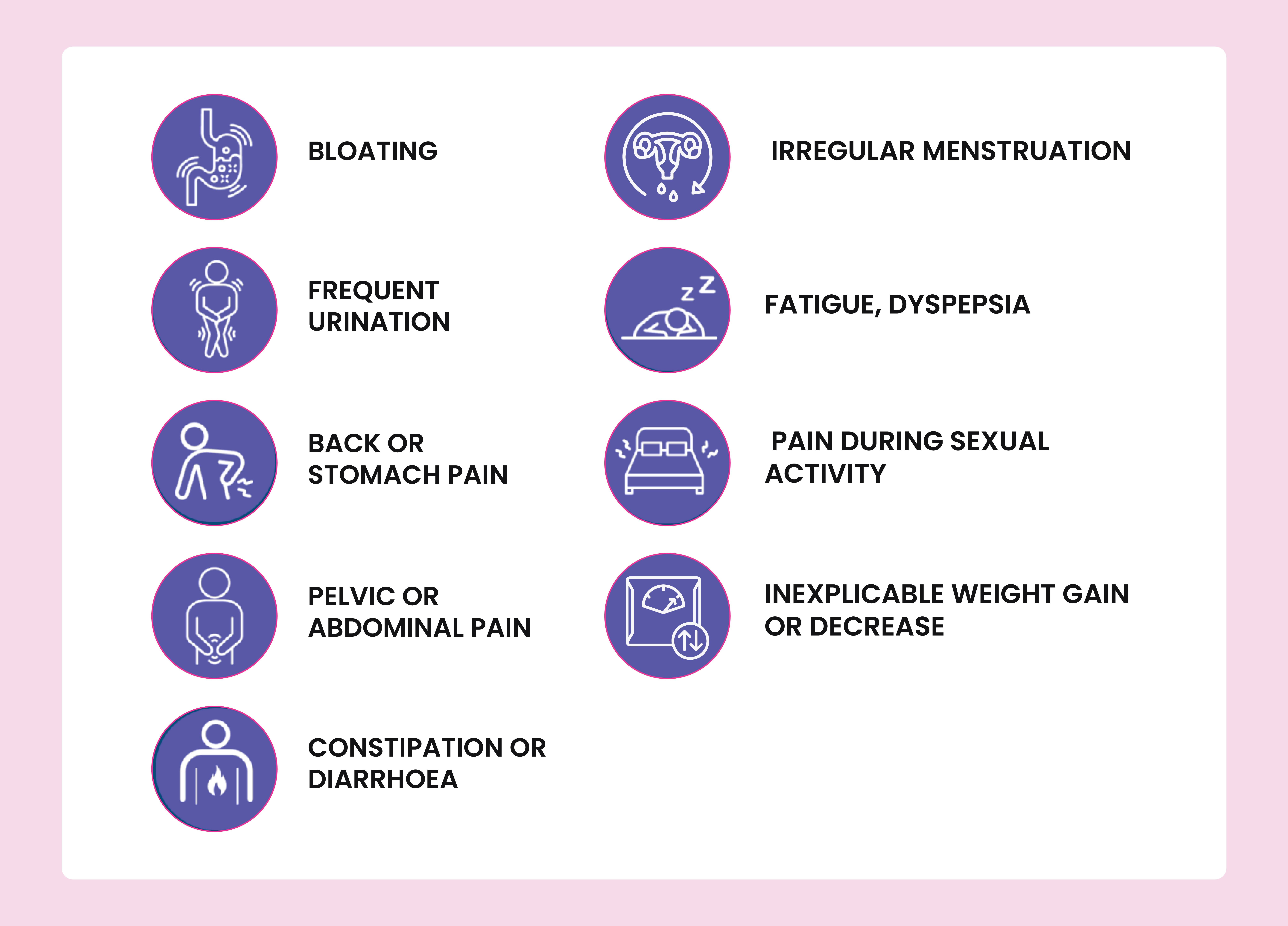
These symptoms might also be caused by other ailments, but if you experience any of them, get in touch with Dr. Manasi Shah, expert in gynecological malignancies in Ahmedabad.
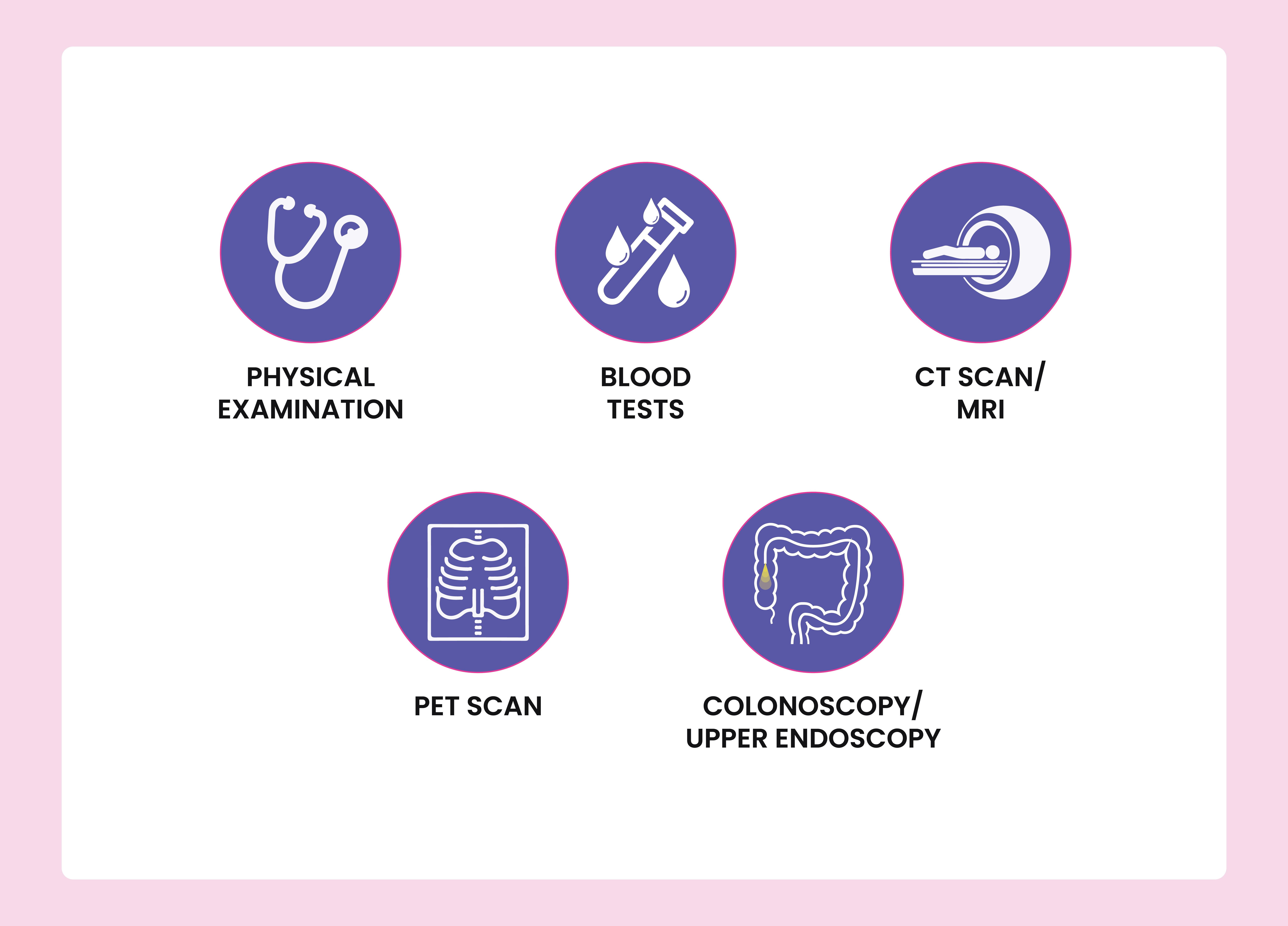
In the event that Dr. Manasi Shah, cancer specialist in Ahmedabad determines that your symptoms could indicate ovarian cancer, the following tests or scans may be recommended to check for cysts, tumors, or other abnormalities:
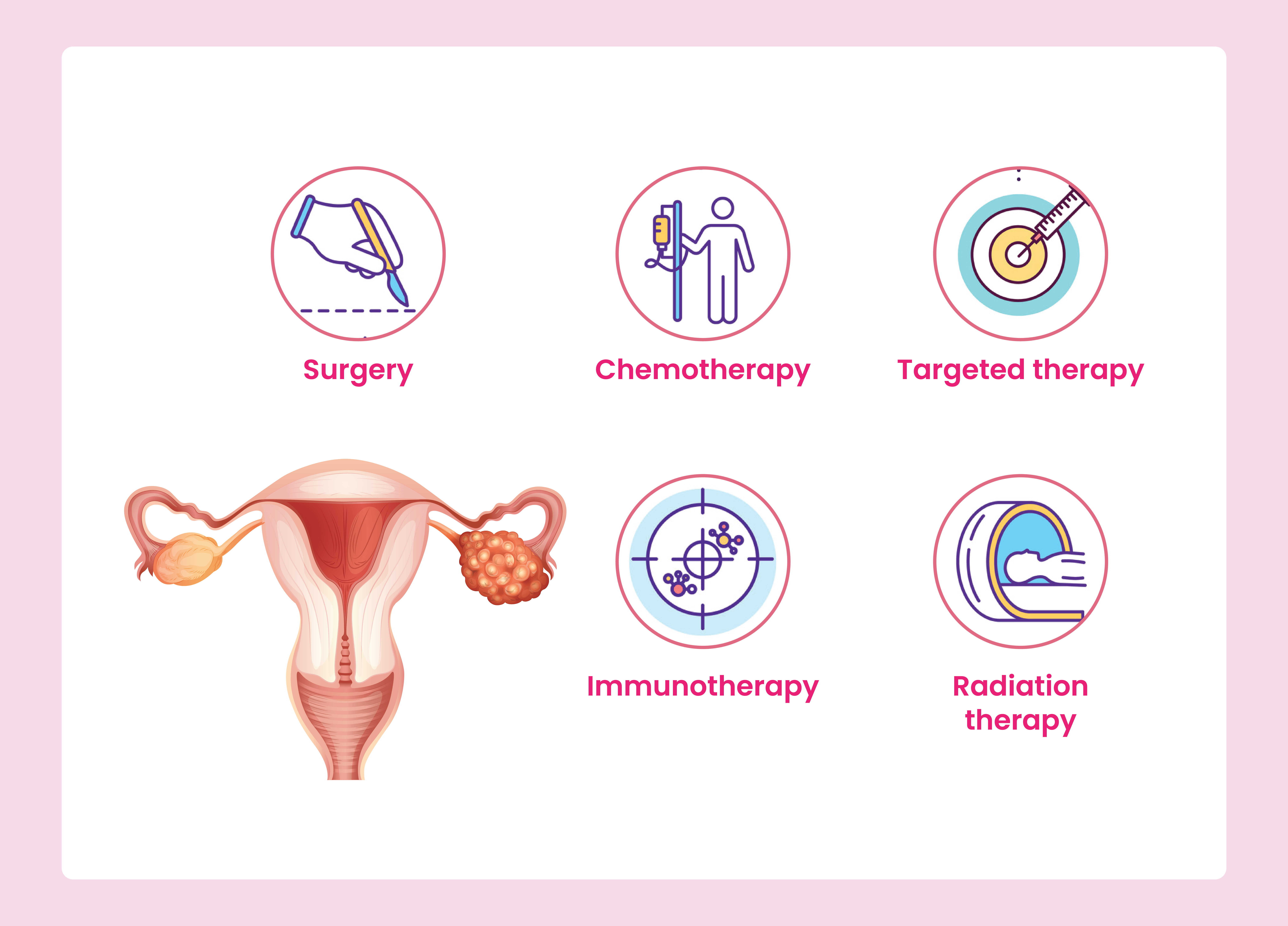
Once the ovarian cancer is found in a patient, the following step is to stage the disease so that a personalized, effective treatment plan may be developed.